Substation Automation Integration Specialists are firms (or business units of large electrical equipment manufacturers) that can assist with or develop and provide a full or partially automated electric power substation on a turnkey basis, leading to “digital substations.” These companies help utilities and C&I firms toward digital substations. Such firms include dedicated businesses (see examples below) or can be business units of larger companies engaged in the electric power automation business as EMS/SCADA suppliers, RTU/PLC/PAC/gateway manufacturers or protection and control specialists. As well, T&D engineering firms, from the nation’s TOP 10 in size and reach, to dozens of smaller but capable regional service businesses are involved in helping utilities and C&I firms integrate and automate (or digitize) the nation’s nearly 70,000 utility T&D substations and another several thousand substations that are managed and operated directly by C&I firms, including large renewables installations.
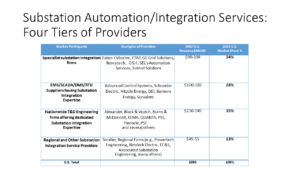
Four “tiers” of substation integration providers are included in our assessment:
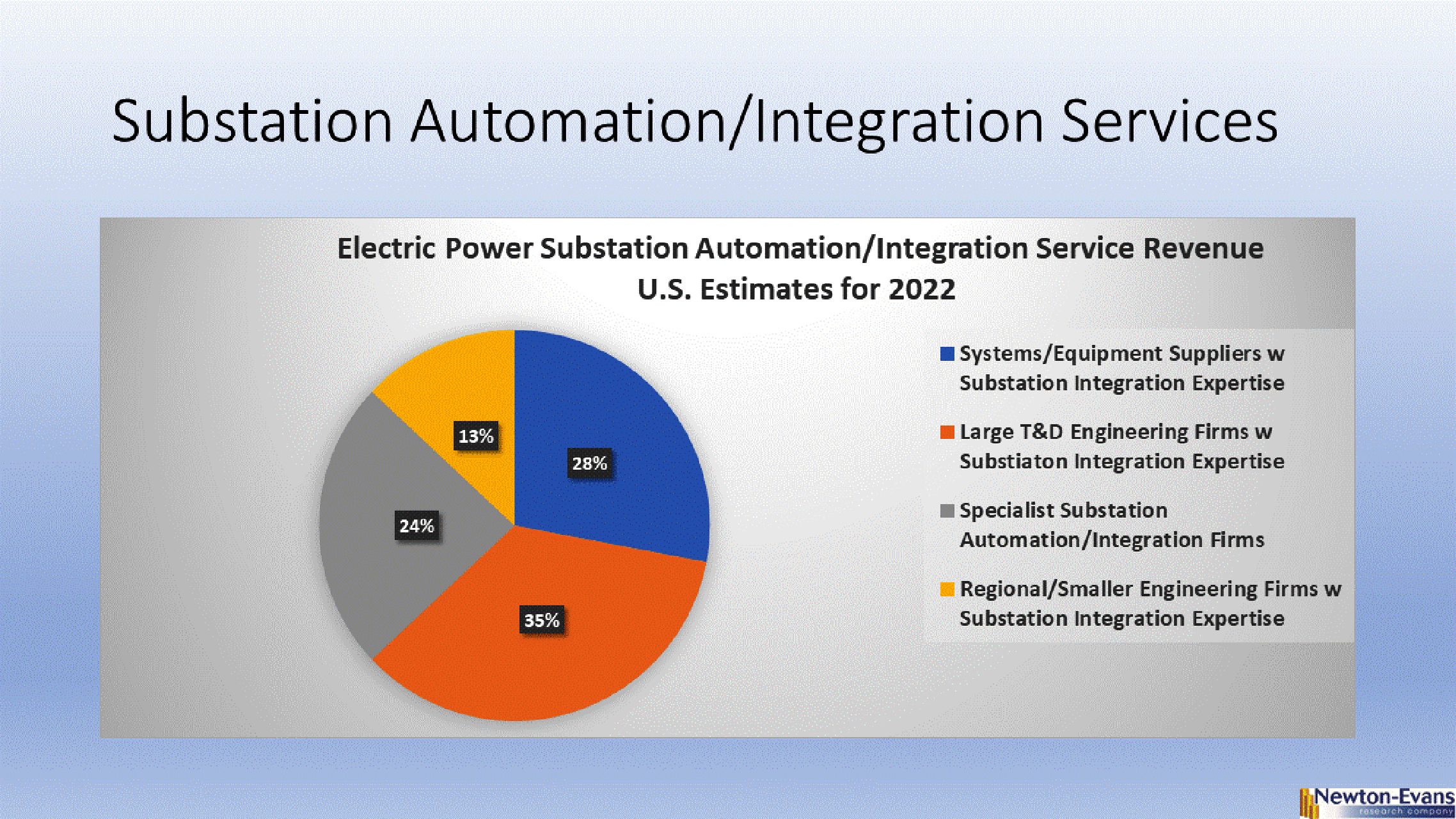
- Specialist substation automation integration service revenues in 2022.es
- SCADA industry participants with substation devices (RTUs, FEPs, Relays, IEDs, platforms) offering substation integration expertise
- National T&D Engineering Services firms with substation integration expertise
- Regional T&D Engineering Service firms
Together, these automation and integration services providers accounted for nearly $400 million of substation automation and integrations services-related revenue in 2022 (Newton-Evans estimate). Click on chart to expand view.
Turnkey costs for substation integration services range from an estimated $45-55,000 for a small distribution substation having few feeders to upwards of $250,000 for a large transmission substation. Some metro-area MV substations with 20 or more feeders can cost upwards of $300,000 to automate and provide device integration services.
The automation equipment/device costs are in the range of $50,000-250,000 for a distribution substation and can range up to $500,000 for smart equipment and integration services in EHV transmission substations.
These totals shown in the chart below for automation and integration services are but a portion of the total expenditures allocated to electric power substations. New substation construction (greenfield) and up-rating activities (brownfield) account for a few billion dollars, while substation equipment and communications costs also account for several billion additional dollars.

 summary reviews and highlights from completed studies
summary reviews and highlights from completed studies
