Looking back over the past 24 months, we initially note what appears to be strong growth in real unit demand for a wide variety of T&D equipment, energy automation systems and related T&D services. Most of this view developed as a result of utility and manufacturer surveying conducted over the past two years. Along with this perceived increase in demand came higher prices and longer lead times after receipt of order by electrical equipment and device manufacturers – affecting the delivery of operational equipment, T&D-related systems and software, and the provision of related services. So, the difficulty comes in trying to differentiate rising end-user dollar expenditures versus rising demand in units of equipment ordered or numbers of systems and services provided.
Higher prices for electrical equipment, automation real systems and T&D services accelerated in the post-COVID era, due primarily to increased costs of materials, ongoing staffing issues (and salary increases), supply chain logjams and, to some degree, slowdowns in the regulatory approval process at federal and state levels.
Separating “real” market growth from increased market values due to inflationary price pressures is often difficult, but surveying both side of the electric power equation to include end-users (e.g. utility + C&I) and industry (manufacturers, energy automation system developers and T&D equipment service providers) enable one to work through this inter-related set of activities to determine real market growth.
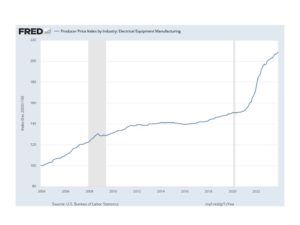
We tend also to rely on FRED (aka Federal Reserve Economic Data) data prepared by the Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis and sourced from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics that includes historical and current price trends for an array of electrical equipment. As shown in the following chart, FRED, as of December 2023, depicts trends for large increases in equipment costs, exacerbated by the COVID-era disruption to the economy, and its effects on the typical economic cycle of capital equipment procurements.
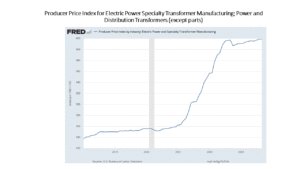
 Now, look at the even more drastic manufacturing cost increases for transformers
Now, look at the even more drastic manufacturing cost increases for transformers
Reviewing these two charts suggests that end-users of capital electrical equipment are spending more because of rising prices. However, there is more to this story. The revenue increases accruing to manufacturers, systems integration firms and T&D service organizations indicate that sales for these firms are moving up, rising faster than inflation, meaning true growth in spending is occurring on orders for additional new equipment and systems and replacement of aging capital equipment and legacy systems.
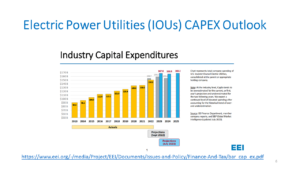
We are seeing growth in unit sales for a variety of equipment and systems and a surge in demand for large power transformers. On the HV side, there is clear evidence that increased procurements have been the case throughout the country for many capital items. A review of EEI’s current CAPEX outlook for IOUs indicated a likely rise from 2022 to 2023 of 10%-11% or so. For transmission, there would likely have been even more growth overall, but delays with renewables projects, transmission permitting issues, and, to some extent, the delays being encountered with large power transformer orders, prevent even more significant transmission interconnection-related growth. (Click on the chart to expand the view).
As to specific growth areas related to HV or transmission-related capital equipment, it is interesting to observe that the United States continues to invest heavily on equipment manufactured for the lower HV ranges as has been the situation for the nearly four decades that Newton-Evans has studied this market. Upgrades to existing transmission networks will mean growth in the EHV and UHV ranges, but it has been a slower upgrade process than was the outlook a decade ago.
In the HV equipment manufacturing arena, there are a relative handful of market participants, with most being global or international firms with the capital reserves necessary to finance multi-million-dollar equipment development and manufacturing costs. This is quite a different picture from the more numerous domestic manufacturers found in most MV or distribution categories of utility infrastructure equipment. As well, there are only about 200 utilities having any transmission assets, and a 10x multiple of utilities providing electricity distribution services throughout the United States.
As a result of an increased number of suppliers competing for equipment orders in the MV equipment range, we see a moderation of inflationary pressure and lower levels of price increases among distribution equipment manufacturers, lower levels than are apparent among the fewer transmission equipment and large power transformer suppliers. Lower-cost-based manufacturers of MV equipment can remain competitive, especially when” price” is the basis for procurements, as it most often is among public power utilities, given product quality remains acceptable and is IEEE/ANSI standards-compliant to end-user buyers.
In addition to the annual capital expenditures for new T&D equipment, there is a flourishing after-market for third party T&D services of all types. There are hundreds of local and regional firms capable of providing services to a wide range of T&D equipment, and scores of these that can provide field-based or in-plant repairs and refurbishments to transformers, switchgear, circuit breakers and the like. The American trade organization for larger T&D equipment services providers is PEARL (Professional Electrical Apparatus Reconditioning League). PEARL is comprised of 61 national and regional T&D equipment refurbishment and service firms. Annual revenues among these member companies total well more than a billion-dollars.
A second association of electrical apparatus services firms is the Electrical Apparatus Service Association, Inc. (EASA) is a U.S.-based, international trade organization of more than 1,700 electromechanical sales and service firms in nearly 70 countries. EASA members sell and service industrial electric motors and related rotating apparatus such as generators, pumps, fans, compressors, gearboxes and blowers. EASA members also provide services for a wide range of T&D equipment, including transformers and switchgear.
Another newer electrical equipment services association is KNOWER, with U.S. members found across the country. While member capabilities center on electrical motors and rotating apparatus, these member firms also provide testing, repair and maintenance for switchgear, relays, and transformers.
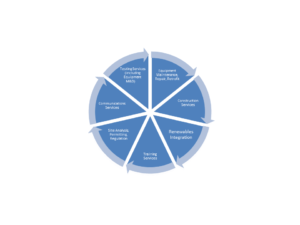
While PEARL members tend to provide excellent services coverage for utilities and C&I firms, EASA and KNOWER tend to focus on the industrial end-user communities, with a focus on electric motors, pumps and the like and provide services to water utilities. The reason I have included an overview of T&D services firms and organizations in this “look-ahead” article is this. As the involvement of more third parties in the process of generation and transmission of electric power continues to increase, there will be a corresponding increase in reliance on equipment service providers that are already well-versed in serving the C&I community. The C&I sector is expanding to include renewable site asset owners together with the site-specific wind plant and solar farm operators. Together, these sites are adding multiple thousands of units of T&D equipment and a hundred or more new substations to the evolving grid each year. Click to expand the view of my T&D services wheel.


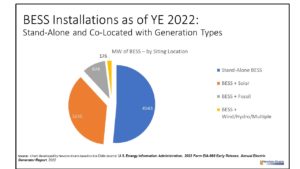
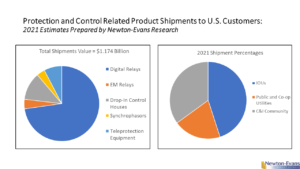
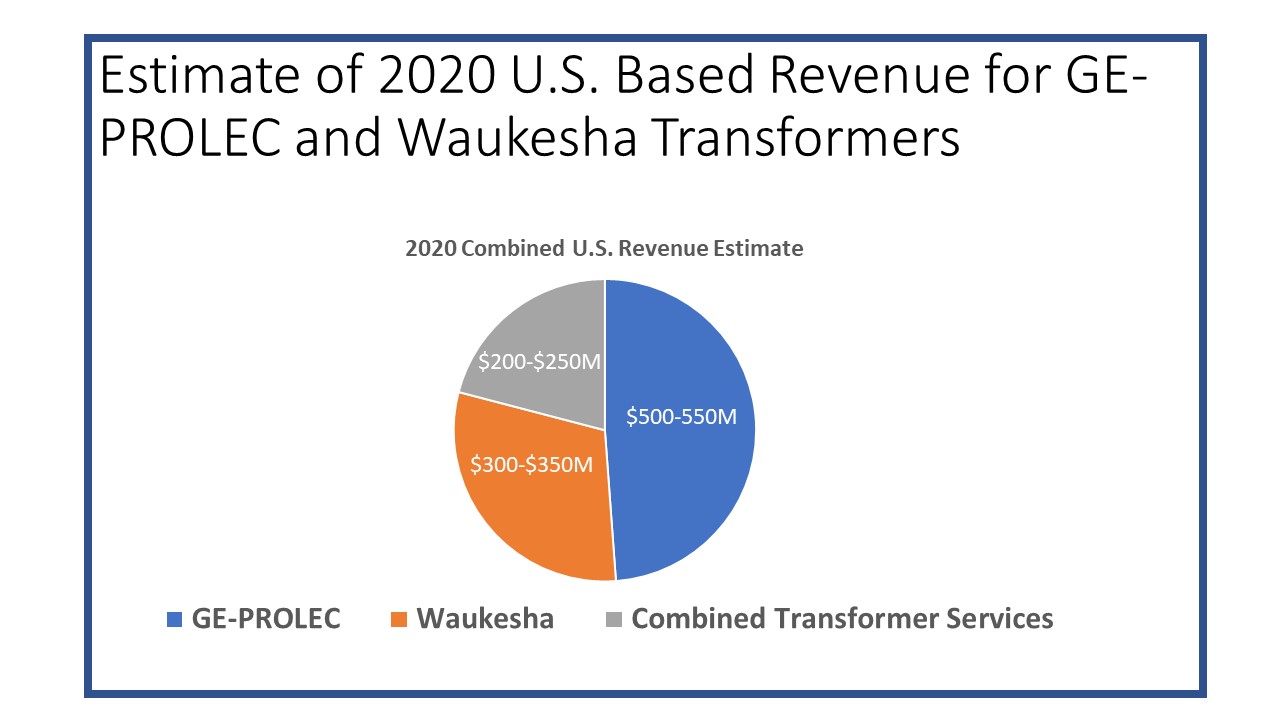

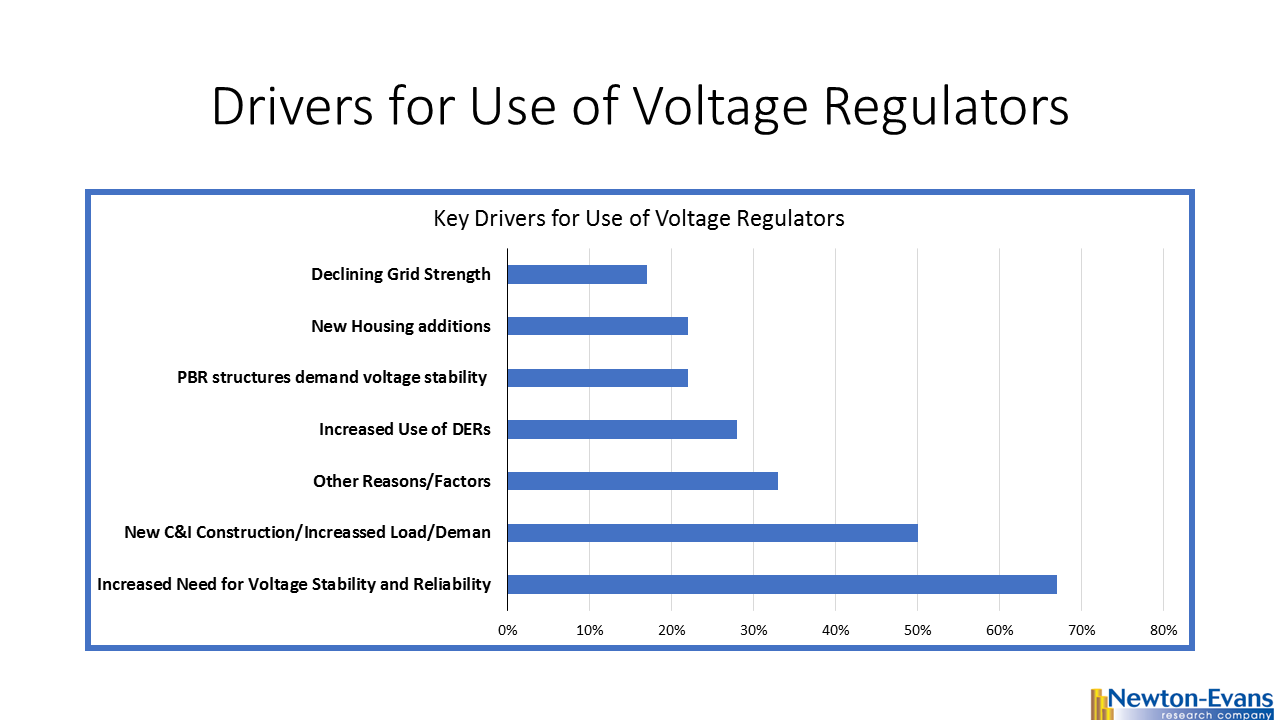 Additional topics being studied include phase-to-ground voltages used in conjunction with VR; the use of VRs with other voltage improvement devices such as distribution feeder capacitors and substations capacitors; purchasing methods and preferences; installation methods, requirements for unit compliance with the latest IEEE requirements, wish lists for new VR product capabilities and a number of other pertinent topics.
Additional topics being studied include phase-to-ground voltages used in conjunction with VR; the use of VRs with other voltage improvement devices such as distribution feeder capacitors and substations capacitors; purchasing methods and preferences; installation methods, requirements for unit compliance with the latest IEEE requirements, wish lists for new VR product capabilities and a number of other pertinent topics.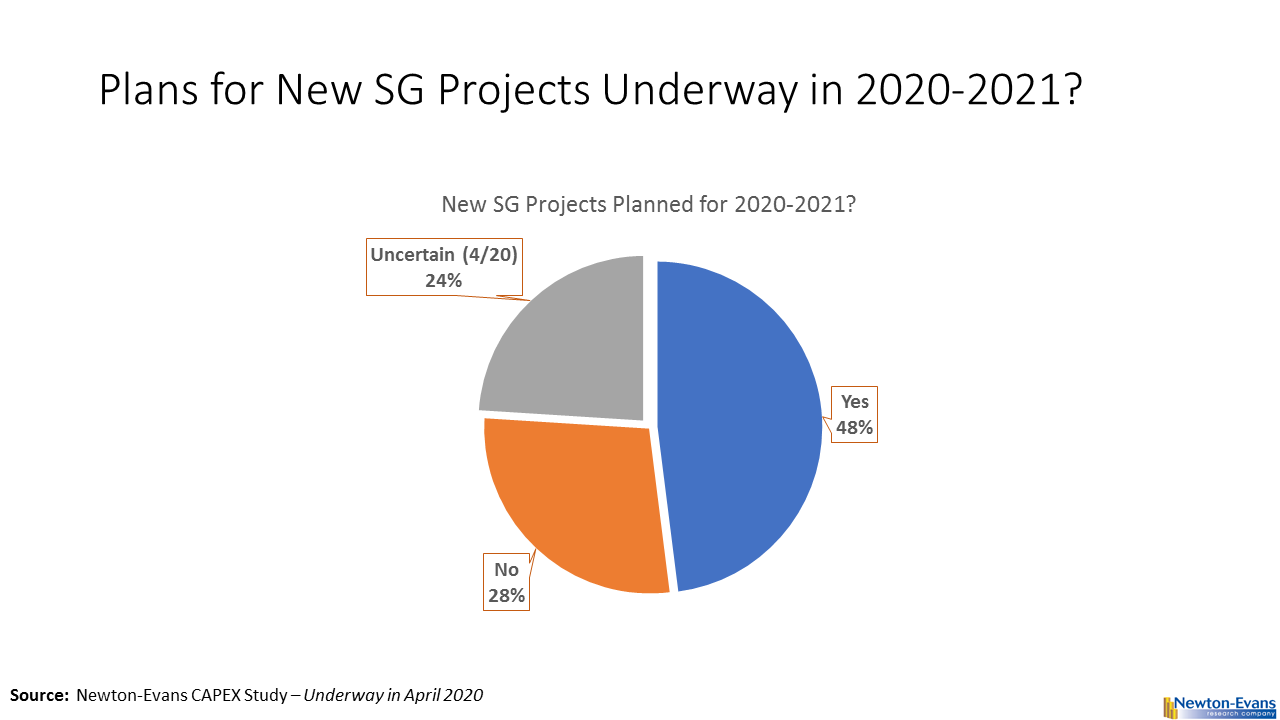
 A special “thank you” gift is is also available for participants at the end of the 12-question (largely multiple choice) survey. To date, we have well-thought-out responses in hand from major IOUs, public utilities and electric co-ops. Looking forward to your survey participation, we thank you kindly for sharing your insights. We are closing off survey data collection work on Friday, May 15, 2020.
A special “thank you” gift is is also available for participants at the end of the 12-question (largely multiple choice) survey. To date, we have well-thought-out responses in hand from major IOUs, public utilities and electric co-ops. Looking forward to your survey participation, we thank you kindly for sharing your insights. We are closing off survey data collection work on Friday, May 15, 2020.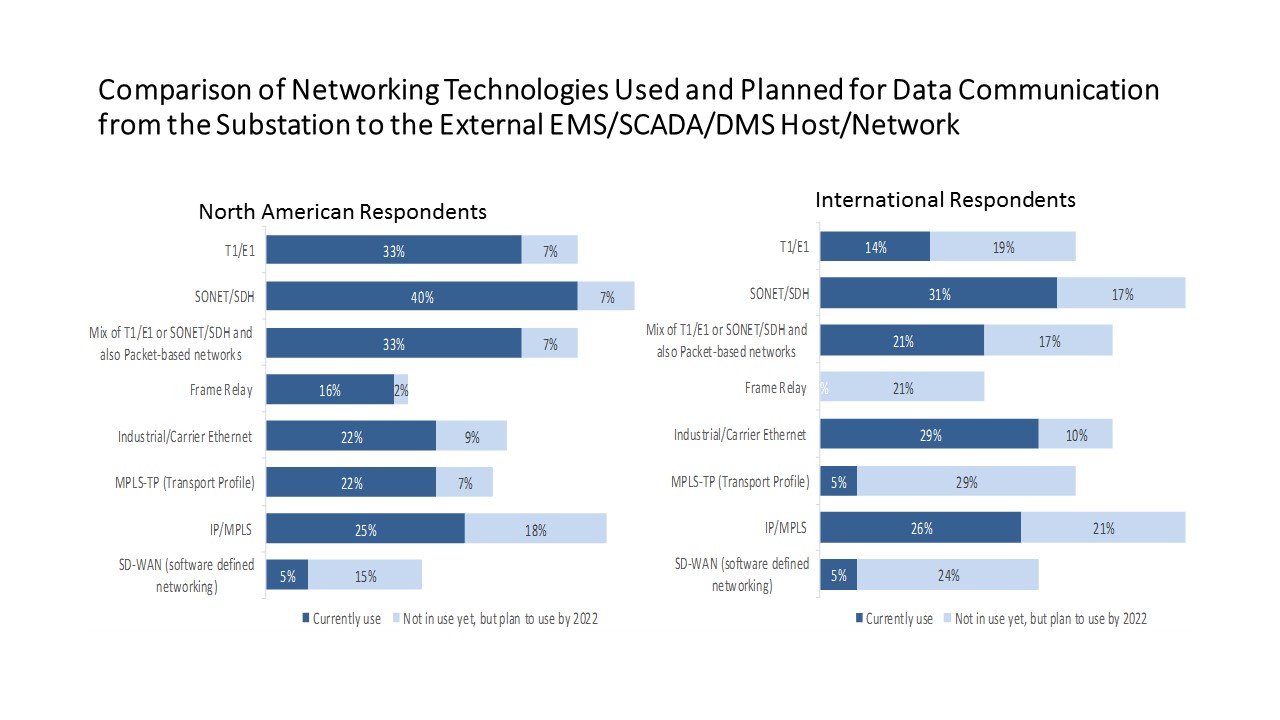 The most prevalent networking technologies used in 2019 among the 42 international utility survey participants included SONET/SDH (31%), Industrial Carrier Ethernet (29%) and IP/MPLS (26%). Based on the survey sample, the leading technologies planned for development by 2020 include MPLS-TP (29%) and SD-WAN (24%).
The most prevalent networking technologies used in 2019 among the 42 international utility survey participants included SONET/SDH (31%), Industrial Carrier Ethernet (29%) and IP/MPLS (26%). Based on the survey sample, the leading technologies planned for development by 2020 include MPLS-TP (29%) and SD-WAN (24%). summary reviews and highlights from completed studies
summary reviews and highlights from completed studies
