As many long-term readers of Newton-Evans’ reports and articles knew from our assessment reported in 2009 there were then three major contenders for the $7 billion Transmission and Distribution business units of the old Areva T&D Corporation. These were the American firm General Electric, the French corporate combination of Alstom and Schneider Electric, and the Japanese company, Toshiba. In the end the French government simply divided Areva T&D in half, and placed the “T” business into Alstom and the “D” business into Schneider Electric.
This past week, there have been widely circulated rumors of another attempt by GE to acquire Alstom’s power business, principally Alstom Power (generation assets) and Alstom Grid, the HV component of the old Areva T&D business. The “D” business of Areva is now squarely in the capable Schneider Electric camp of medium voltage equipment offerings.
Newton-Evans Research believes there could be significant benefits to GE’s efforts targeting the global electric power industry if the company’s current purported acquisition attempts bear fruit. There are four key reasons for this view, in our opinion:
(1) As reported by others, GE will gain improved access to European and other world regions with long-established relationships nurtured under the French management and policies, which are likely to continue under GE ownership.
(2) GE Energy Management will again be able to lay claim to some real growth within 24 months. These increases will come from both inorganic growth (via this potential acquisition – itself worth about $4.5 Billion in current year sales of Alstom Grid products, systems and services) and organic growth (through increased interest and procurement of all GE Energy Management equipment, products and services). The four component businesses of GE Energy Management include: Digital Energy, Industrial Solutions, Power Conversion and Energy Consulting. These will each benefit significantly.
(3) GE will be able to fill several significant product/equipment gaps in its electric power transmission and distribution product line and related automation offerings. This will result in significant mid-term benefits to GE Digital Energy.
(4) Alstom’s power business includes assets for power generation such as turbines for coal, gas and nuclear power plants, and wind farms. Alstom Grid offers a world-class group of control systems for power transmission and distribution as well as many leading transmission-class equipment offerings. The company’s “e-terra” line of systems is the leading market shareholder among critical systems used in the global electric power industry.
A successful acquisition by General Electric would provide the firm with world-leading combined market shares in substation automation, protection and control and T&D control systems (energy management and SCADA). GE Energy Management would become a major player in several growing portions of the transmission equipment business, establishing a stronger foothold in the North American and international transmission market segments described below. Together these segments are worth $32-40 billion on a worldwide basis. Newton-Evans’ estimates that Alstom Grid earned about $3.5 billion to $4.1 billion in HV equipment sales in 2013.
FACTS and Reactive Power Compensation: ABB is probably the global leader in flexible AC transmission systems and the related reactive power compensation segment of high voltage equipment for transmission networks. Siemens Energy is a strong number two supplier with several others (notably Mitsubishi Electric Power Products, and American Superconductor) also active in North America, and around the world. Alstom Grid and GE are also participants that together could challenge the market leading positions of ABB and Siemens within three years of a merger of product lines.
HVDC Equipment: Siemens is the market leader in HVDC, with ABB a reasonably close second place share holder and MEPPI the likely third most important player. However, an integrated Alstom Grid-General Electric product grouping would enable the company to attain up to a quarter of the available market shares.
Gas Insulated Substations/Switchgear: The North American market for High Voltage GIS equipment is in excess of a quarter billion dollars. While Alstom Grid has only a small share (stronger in Canada than in the US), GE Energy could now present itself as a player in this growing market segment of high voltage switchgear. GE would also play a much more important role in international markets where – unlike in North America – GIS equipment is prevalent. Globally, GIS equipment is a 2-3 billion dollar annual market.
High Voltage Bushings: This relatively small (about $125-150M in annual worldwide sales) market is led by Siemens and ABB. However, the combined Alstom Grid and GE offerings could make GE into a formidable player in this segment.
High Voltage Capacitors: GE Energy is already the major participant in the North American market for HV capacitors, but globally, ABB is the leader. Alstom Grid, by virtue of its recent acquisition of the Finnish manufacturer, Nokian Capacitors, is also a very strong player in Northern Europe. Together, the product lines could pose a real threat to ABB dominance here (yet another billion dollar global product segment).
High Voltage Circuit Breakers: Alstom Grid is already a major player globally, and with GE’s “sales boots on the ground” could significantly increase its share in North America and abroad. ABB and Siemens are both very strong manufacturers in this large annual global market of better than $2 billion.
Disconnect Switches: High voltage disconnect switches are vital components of many transmission systems, and the global market runs to about $500 million annually. GE and Alstom Grid are among the six leading suppliers of disconnect switches in North America, but lag behind Hubbell, S&C and Southern States, some of which offer circuit switchers used for disconnect applications.
Instrument Transformers: The market for high voltage instrument transformers had been dominated by specialist “independent” manufacturers until recently. A recent buying spree had Siemens acquiring Trench Electric, Alstom Grid acquiring Ritz and ABB acquiring Kuhlman. Currently, the market for HV IT equipment is shared primarily by these three firms, with GE very active in the MV segment. Together, the combined HV/MV instrument transformer offerings of an integrated GE-Alstom Grid would change the shape of this market, which in North America alone hovers around $100 million, and close to one-half billion dollars worldwide.
Air Core Reactors: Another component of some transmission network architectures, Siemens-Trench and Alstom Grid-Ritz are key players, with GE also strong and MEPPI further behind, but with a growing share. A number of smaller participants account for a rather large share of this $400 million global business.
Surge Arresters: Another sizable market in its own right (about $1 billion per year globally) high voltage surge arresters are manufactured by a number of US-based firms such as Hubbell, Thomas & Betts, and Cooper Power, each of which competes quite successfully against the likes of ABB, Siemens and GE.
Automation Systems: GE’s long-established XA/21 EMS platform and Alstom Grid’s highly rated E-Terra offerings are both held in high regard, although GE’s systems are mainly installed in the USA. Earlier (1990’s era) acquisition efforts have been fraught with initial business unit integration problems (to wit- ABB with its acquisition of the older Ferranti EMS business (Spider v. Ranger offerings) and Siemens-Control Data (Sinault-Spectrum v. Empros).
Protection and Control: Internationally, Alstom Grid (with part of the Stafford, UK-based relay business) holds an estimated 16% share of the global protective relay market, estimated by Newton-Evans to be about $2.2-$2.4 billion on an annual basis. GE Multilin, based in Toronto, is also a very strong market participant, especially in the Americas, and is the leader in industrial protection and control markets.
T&D Services: GE is a major participant in T&D equipment repair and services, especially with its transformer repair business, and Alstom Grid outside of North America earns about $550 million per year with its array of high voltage equipment services and automation systems maintenance agreements.
We will soon see learn whether and how the French government will allow Alstom to sell off all but its transportation business to a “foreign” company. GE will likely have to make significant concessions regarding job retention among the French workforce. This could have ripple effects on its global workforce.

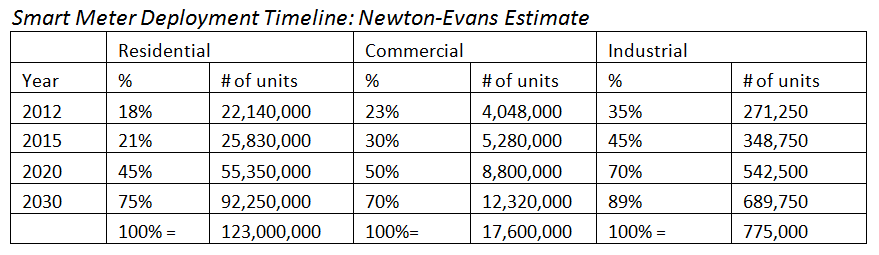
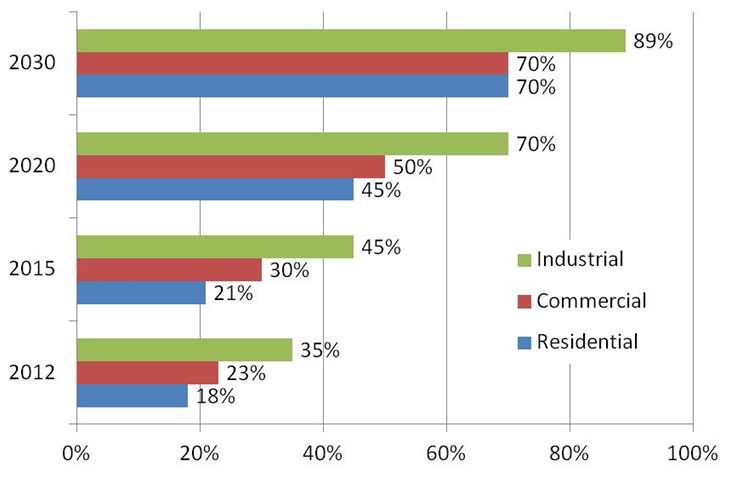
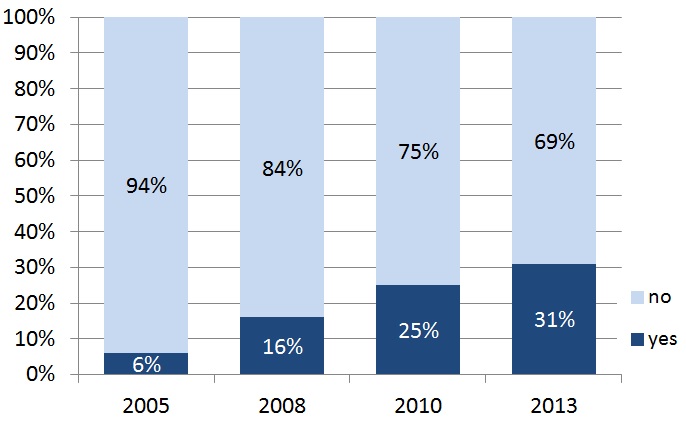
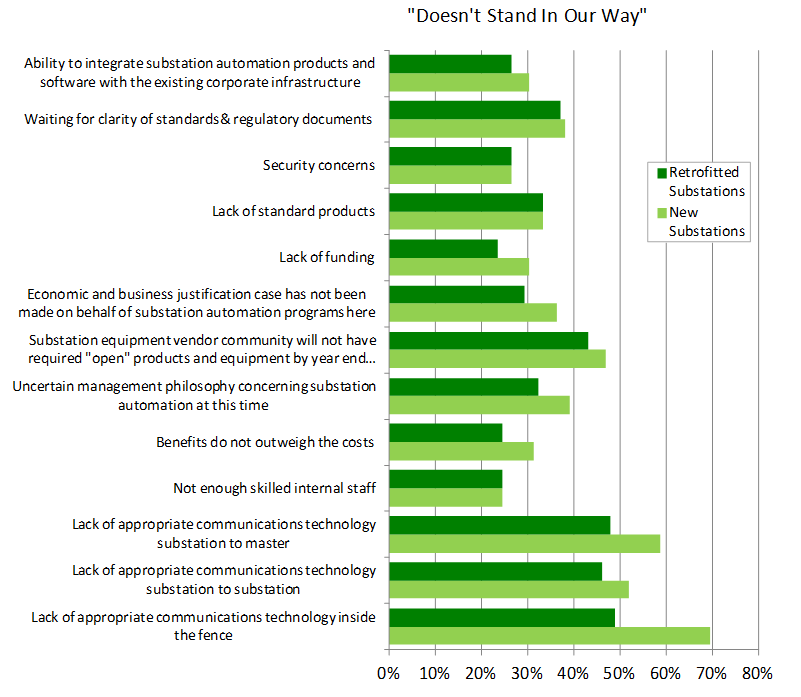

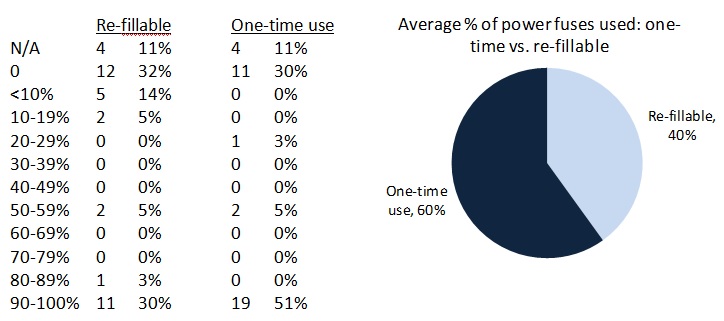
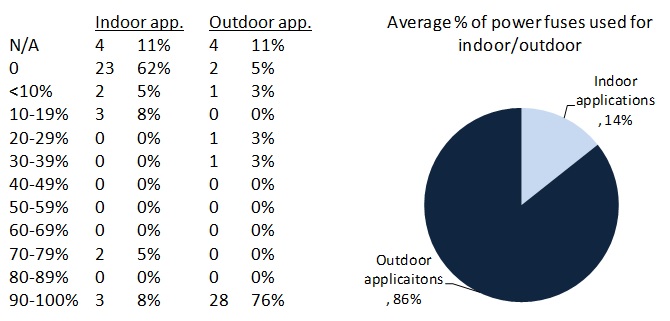
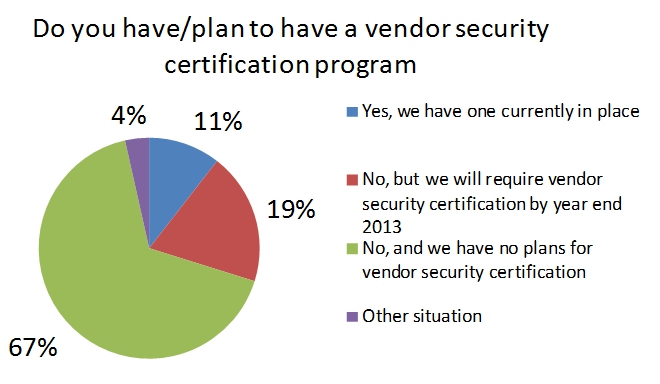

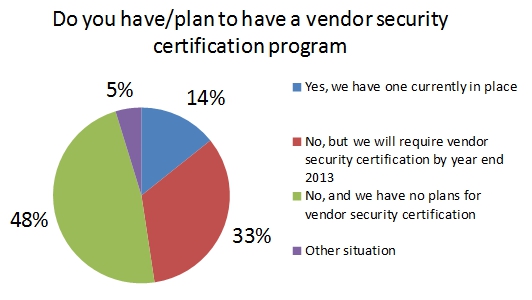
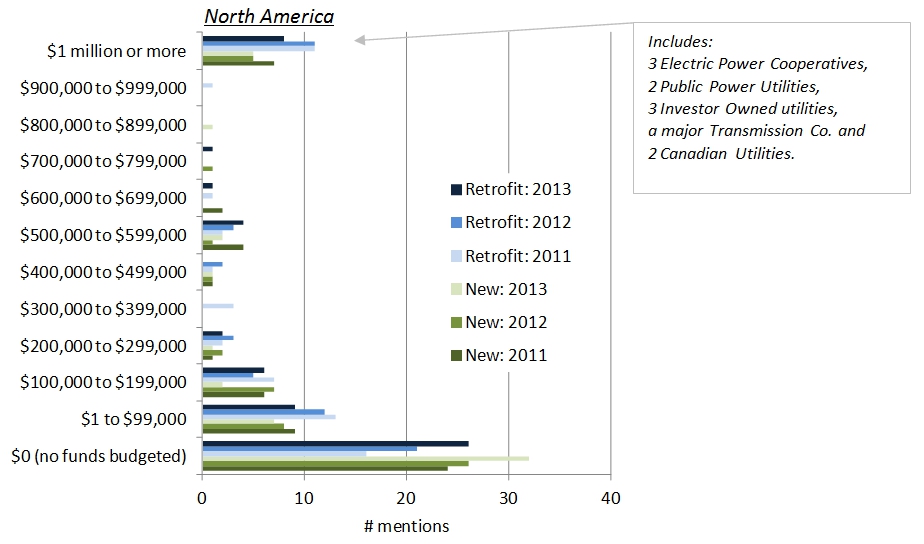
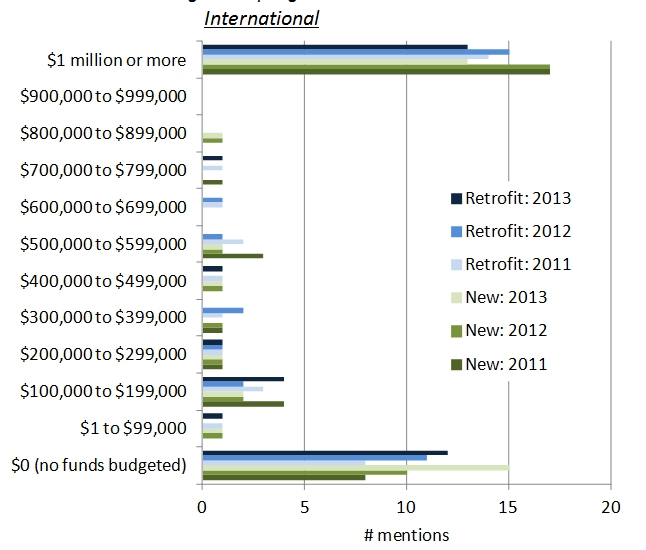
 summary reviews and highlights from completed studies
summary reviews and highlights from completed studies
